Turning a good design into a great product requires more than just an innovative idea. It requires collaboration, precision, and the right material. Our Engineering and Design Team demonstrates excellent knowledge of tooling for die casting and engineering in zinc. We have years of experience as one of the USA’s top zinc die casting companies.
For industries looking to enhance strength, durability and efficiency, zinc design is often an under-utilized solution. With its unique advantages of zinc die casting, Deco Products helps engineers optimize designs from start to finish.
With over 20 engineers and over 400 cumulative years of experience. Your next new product or tool transfer project is in good hands with our engineering design process.
Early involvement of Deco’s engineers helps turn innovative concepts into optimized design for successful die casting production. From material selection to managing tolerance, zinc design offers unique benefits that improve product performance and cost-efficiency.
When designing a new part, our engineering staff works with your engineering team. We work diligently to determine if zinc is the best material for your design.
Our engineers get familiar with your part, and its end use along with your project requirements.
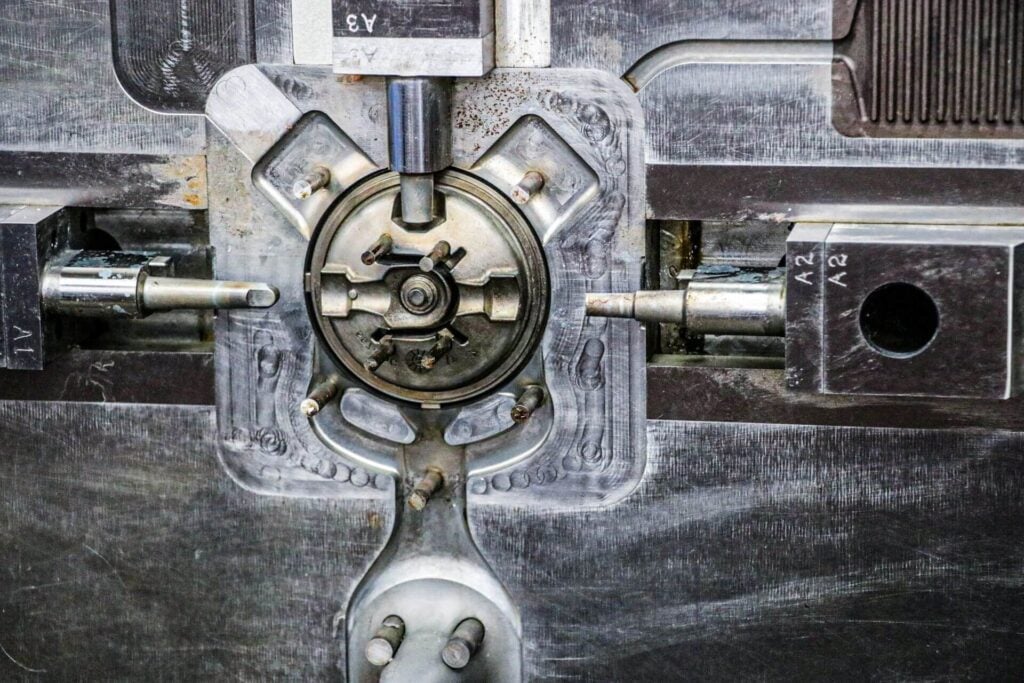
We then help optimize the design for low initial cost and long-term value. We take into consideration different types of die cast tool design, tool life and ongoing long-term quality.
Both with new tooling designs and tooling transfer projects, our team has seen it all. Frequently we can adapt the existing tool to one of our over 100 die casting machines.
With many machines we have high diversity of options. In some instances, implementation is not easy for a tool transfer. Our team uses experience and creativity to adapt the current tool while ensuring a rapid, but also reliable solution.
Our engineering and tool room experts are reliable. They have completed many successful tooling transfer projects over the years!
Deco continuously pushes the USA die casting industry and our own processes for increased efficiencies, capacities, and capabilities.
We are data centric with continuous improvement ideas and projects. We invite our customers to visit us to see the possible next great idea for implementation.
When choosing between casting metals, understanding the advantages of zinc die casting alloys is key. Zinc’s physical and mechanical properties make it ideal for complex designs and high strength applications. Here is how it compares:
Casting with zinc is a more cost-effective solution than machining. It allows for faster production with thinner walls and fewer post-production processes, which translates to cost savings. Die casting production offers quicker cycle times and fewer machining operations than traditional methods.
Compared to aluminum alloy and magnesium, zinc shines because of impact strength, longer tool life and lower melting temperatures. These characteristics lead to cost-effective production, especially in high pressure environments where strength and durability are key.
Zinc’s ability to handle high pressure also makes it ideal for hot chamber die casting. Which allows for faster production rates and improved efficiency compared to aluminum or magnesium die casting.
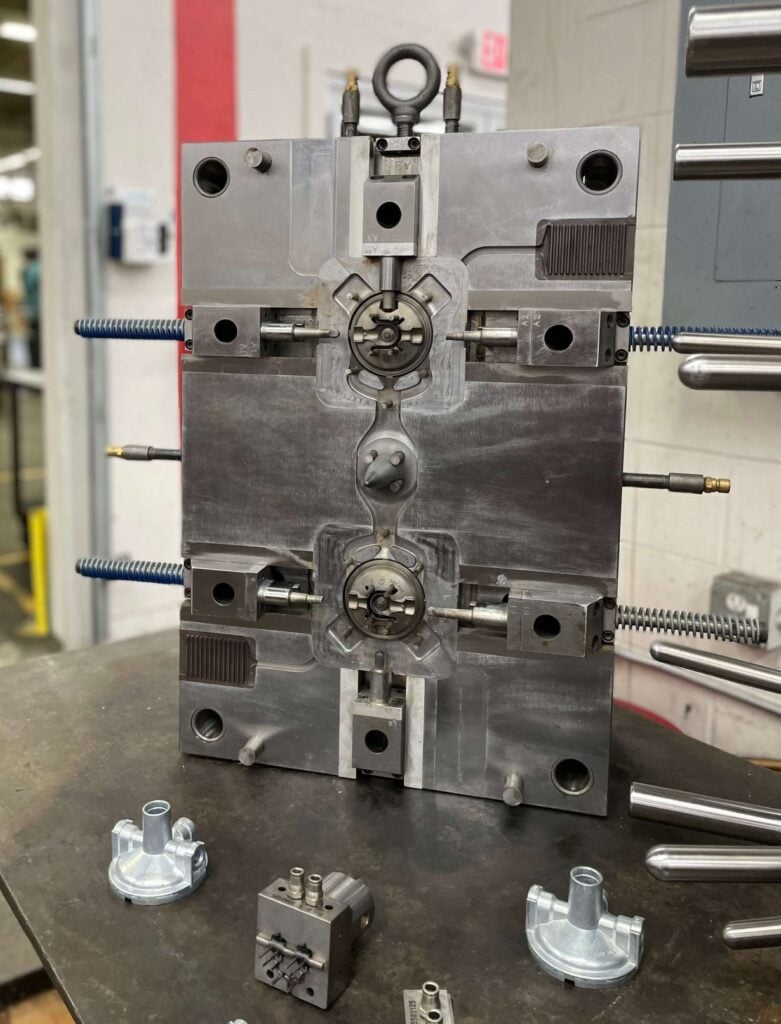

Die casting tool design is a key component in your project success. Our engineering and design team work directly with customers during the design stages. Our team ensures optimization of the tool design for consistent quality and lower final product cost.
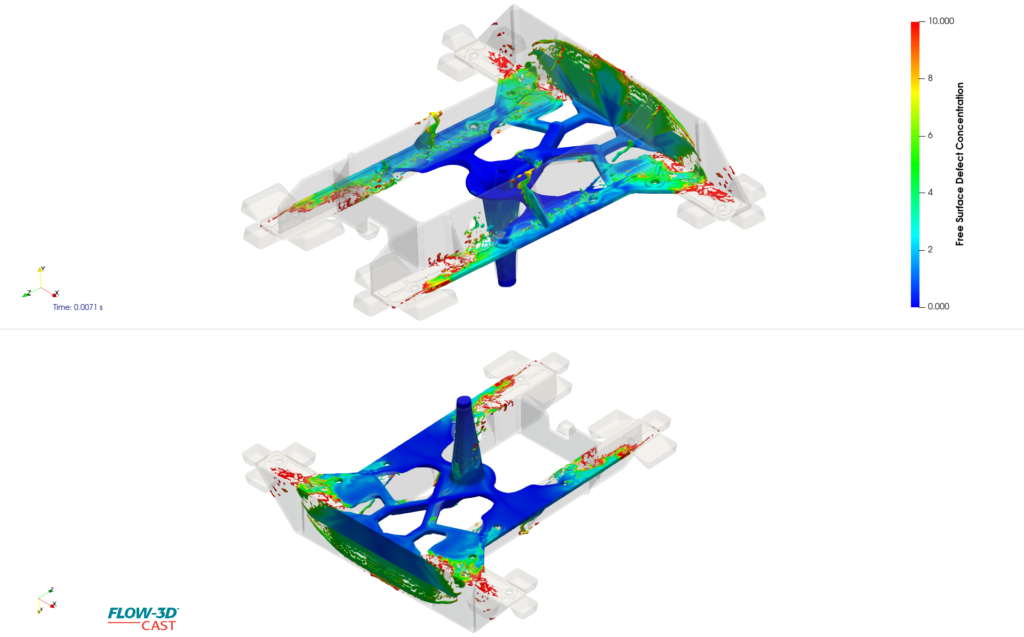
We use Flow-3D Cast simulation software which allows us to analyze the metal flow of the zinc and tool design. This software is critical in creating superior die casting molds and products.
Some of the most challenging simulations for accuracy revolve around metal casting applications. It all starts with a logical sequence that closely follows the sequential key processes. We take into account the complex range of the physics involved along with the challenges of thin-walled castings.
We focus on the simulation of our hot chamber method to discover and accurately predict filling and solidification. We then apply the best modeling workflows to allow us to meet your specifications.
Deco Product’s engineering and design team collaborates closely with customers to optimize design for manufacturability. Key considerations include:
Involving Deco’s engineers early ensures high quality parts with minimal revisions, reducing costs associated with reworking and material waste.

Using advanced mold flow simulation software, Deco can visualize zinc castings inside the mold before production begins. This speeds up the design process and ensures optimal part fill and number of cavities. By spotting potential problems early, like air entrapment or weak spots, we can extend tool life and lower maintenance costs.
The die casting process for zinc benefits from zinc’s lower melting temperatures, which significantly extends tool life. Deco’s use of hot chamber die casting allows for faster cycles, reducing wear and tear on tools. In comparison, tools used for aluminum alloy castings experience more rapid degradation with the higher temperature required.
Our process including simulations help to refine part design for better part quality. Ensuring that the final product meets both performance and aesthetic expectations. This reduces the risk of defects such as blisters or voids, resulting in a stronger, longer-lasting product.
Clear communication is essential throughout the design process. Deco Products emphasized regular interaction with customers to ensure the designs meet all expectations. Customers can provide feedback by seeing the design before they finalize it, especially when they involve mating parts. This collaborative approach allows Deco to suggest subtle changes to improve use-case performance without altering the core design.
A major benefit of zinc is a long tool life. Zinc alloys have a lower abrasiveness resulting in less die cavity erosion of the steel tool. A key question to answer is what is your usage for your component?
Zinc molds average up to a million shots per tool. Making zinc an excellent return on investment for high-volume castings with EAU over 50,000.
By comparison aluminum die castings may achieve 10% of the same tool life to zinc high usage castings.
When strength and structural integrity are crucial to your part design, zinc provides excellent strength. Manufactures recognize zinc die cast parts for their mechanical strength and high tensile strength.
Zinc produces parts with precise detail, thin wall thickness and allows for optimal structural integrity. Die casters know that these alloys can withstand heavy loads while retaining their structural integrity.
During high-pressure die casting zinc alloys achieve a smooth surface. This finish impacts the aesthetics and function of the part. Zinc is one of the better metals for applying decorative finishes such as powder coat or plating.
Whether your part finish is raw, or decorative zinc alloys are the right choice for your die cast project.
Zinc is higher density metal. The sweet spot is components similar in size to a bolt that is 1/2 x 1/2 x 1/2 inches. This extends up to a part similar to a gas regulator that would be 4x4x4 inches.
Zinc’s higher density is a contributing factor in its superior impact resistance. The advantage to this density is if your design requires stability or more of a substantial feel.
Zinc is not typically the material of choice for parts that are big or above 8 lbs.
Zinc alloys have the ability to cast to tight tolerances. This net shape manufacturing process reduces the need for costly machining. Because the part design can include 3 dimensional features.

Zinc alloys are particularly well-suited for parts that require toughness, rigidity, and high production. Zinc parts are also highly environmentally friendly because of their recyclability.
The zinc die casting process is cost-effective. Producing lightweight and strong parts. These parts often outperform those made from aluminum, plastic, or other materials.
This Deco advantage catapults our customer partnership beyond what other zinc die casters support and is key to Deco’s value proposition and mutual long terms success of our customers and Deco!
Deco Products is a full-service zinc die-caster that offers precision zinc die-castings to customers globally. We utilize custom-designed hot-chambered die-casting machines to offer you competitive and quality products.